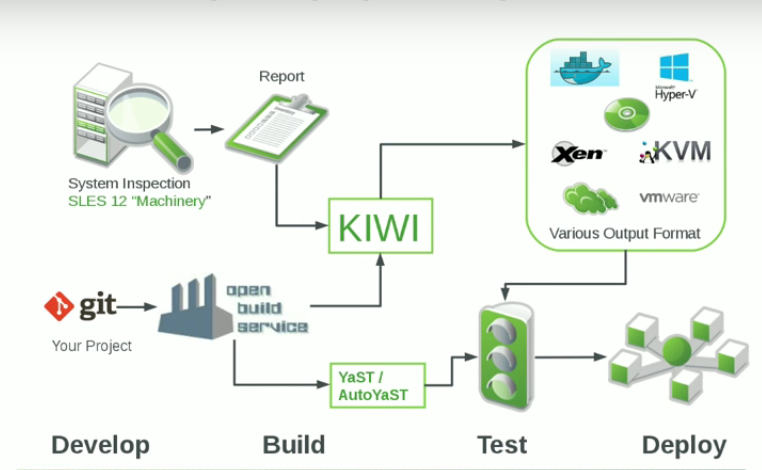
Rest assured, Kiwi is neither a bird nor a fruit in the OpenSUSE world! Kiwi is an open source project licensed under the the GPLv2 and it is written in Perl. The project is sponsored by SUSE to build OS image and Appliance. “The KIWI Image System provides a complete operating system image solution for Linux supported hardware platforms as well as for virtualisation systems like KVM (Qemu), Xen, or VMware. KIWI is a command line tool and is the backend of SUSE Studio. The project is sponsored by SUSE. “ – OpenSUSE. OS images are heavily used in cloud environment whether you need a .vmdk .img .ovf or even a raw file etc.. In brief, Kiwi provides a raw disk images with no additional configuration needed. The idea of the Kiwi project is to maintain efficiency duing the development , building, testing and deployment phases
The kiwi tool itself is a command line tool, however, the SUSE Studio web app provides the GUI facility. Let’s now get on some basic commands.
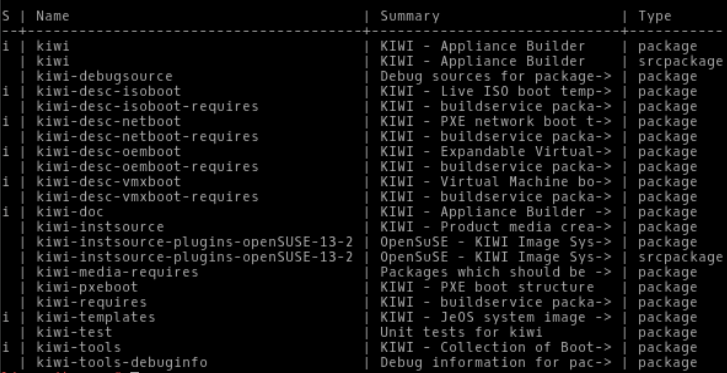
1.To check packages installed on your machine for Kiwi do a zypper se kiwi. These are the packages I got for ‘S’ in means state in the first columns and ‘I’ for installed
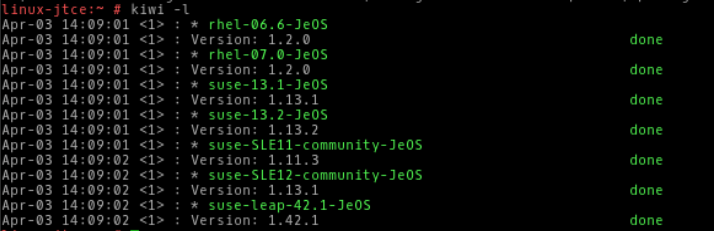
2. To list all templates available, do a kiwi -l As you can see i have templates for the RHEL and SUSE environments. There are other templates available on the Open build service repository.
3. The template locations on an OpenSUSE machine will usually be at /usr/share/kiwi/image where you will find another directory say rhel-06.6-jeOS and some configuration files are found there for the boot process. The file config.xml will gave your an overall idea of which repository, packages etc.. you are going to use with your templates.
4. So, lets create a suse-13.2 vmx file file with kiwi. The following command is building the image. The parameter -d is the destination and the –type is simply the type of the image. I also created a directory /kiwi Point youself in the directory /usr/share/kiwi and launch
kiwi –build image/suse13.2-JeOS -d /kiwi –type vmx
5. Once the build is finished, you can use the .vmx file to run your machine.
There is also a KIWI cookbook free for you at this link made by Marcus Schäfer which is really interesting. The SUSE Cloud stack will also give you several tools to run and test your images. The OpenSUSE stack environment provides facilities for mixed distros. The SUSE Studio is a collection of tools designed to improve the efficiency of building managing and maintaining software virtual and cloud applications.