This is another blog post to break into part the VCA Data center Virtualization training. So far articles already published are:
- An introduction of Data Center Virtualization
- Components of VMware vSphere 6.0 – part 1 which include an overview of Vsphere 6.0, its architecture, Topology and configuration maximums.
- Components of VMware vSphere 6.0 – part 2 which include an introduction to vCenter servers and its features.
- Components of VMware vSphere 6.0 – part 3 which include Shared Storage, Shared Protocols, Data Stores, Virtual SANs and Virtual Volumes
- Components of VMware vSphere 6.0 – part 4 which include Networking feature in vSphere, Virtual Networking, Virtual Switches, Virtual Switch types and Introduction to NSX
- Components of VMware vSphere 6.0 – part 5 which include vSphere Resource management features, vMotion, DRS, DPM, Storage vMotion, Storage DRS, Storage I/O control and Network I/O control.
This part will address with the following topics:
- vSphere availability features
- vSphere data protection
- High Availability
- Fault tolerance
- vSphere replication
vSphere availability features
VMware vSphere delivers maximum availability of your virtualized environment making unplanned downtime of thing of the past. The enhanced availability also minimizes unplanned downtime through automated virtual machine restart. Automatic virtual machine placement and load balancing, Backup and Recovery and Site wide Disaster recovery enhances availability. The vSphere availability features include vSphere Data Protection, High Availability, Fault tolerance and vSphere replication.
vSphere Data Protection
VMware vSphere data protection is a robust easy to deploy disk-based backup and recovery solution for VMware virtualized environment. The feature enables both local data protection and off site disaster recovery. Backups are performed locally and then replicated offside for disaster recovery. Data Protection is managed using the vSphere web client, an interface that is familiar to the vSphere administrator. With data protection, tasks such as creating Backup jobs, Restoring virtual machines and Backup data replication are intuitive.
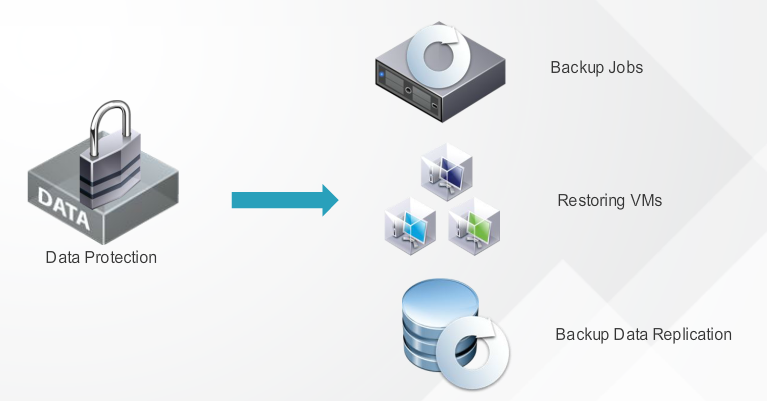
Data protection includes agents that enables application consistent backup and recovery from a wide variety of servers including the Microsoft SQL server, Microsoft Exchange server and Microsoft Sharepoint server. It allows you to restore the replicated backup data to a target location or back to the source location. This functionality provides several retention and recovery options to satisfy a wide variety of business requirements. Data protections also include automates backup verification schedule jobs that routinely restore virtual machines, boot the guest operating systems and check for VMware tools heart beats to verify if the virtual machines have been recovered successfully and then delete the restored virtual machines. The data protection support for backup data storage provides increased reliability and backup data capacity with minimum impact on network bandwidth and performance.
High Availability
High Availability proposes easy to use, cost effective high availability for applications running on virtual machines. In the event of physical server failure affected virtual machines are automatically restarted on other server with space capacity. In a case of operating system failure, HA restart the affected virtual machine on the same physical server.
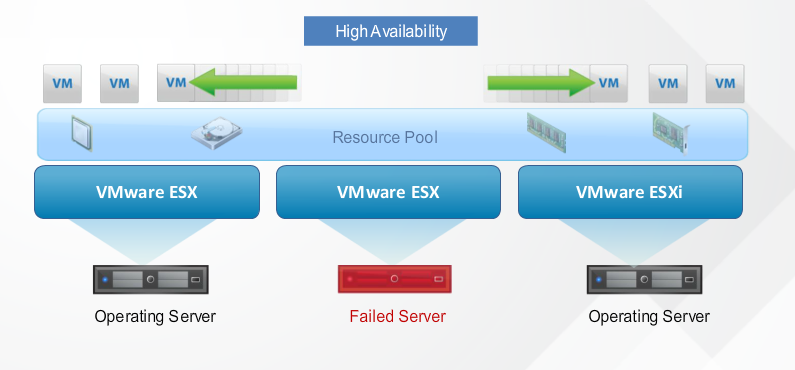
The combination of HA and the other availability features of the vSphere platform provides organisations with the ability to select and deliver the level of availability required for all their important applications. HA enables you to minimise unplanned downtime and IT service disruptions. While eliminating the need for dedicated standby hardware or the installation of additional software. It provides affordable and uniform HA across the entire virtualized IT environment without the cost and complexity of fail over solutions tie to either operating systems or specific applications. To monitor operating system failures, HA monitor heartbeat information provided by the VMware tools package installed on each virtual machine on the cluster. Failure are detected when no heart beat received from a given virtual machine within a specified time interval.
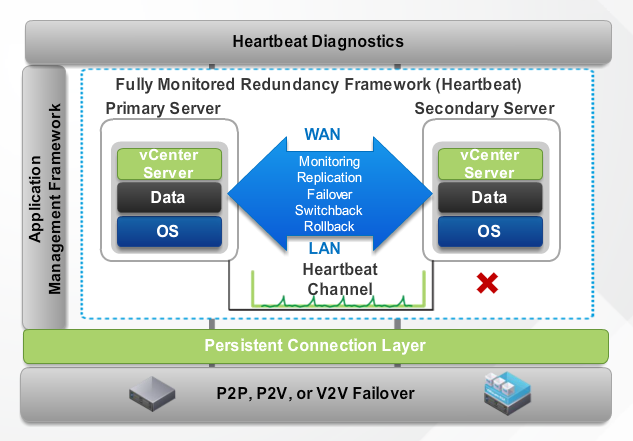
Fault Tolerance
vSphere Fault Tolerance is an important feature that allows you to protect mission critical high performance applications regardless of the operating systems or other running applications. It provides continuous availability for applications in the event of physical server failures by creating a lock step of virtual machine that is always up to date with the primary virtual machine. In the event of hardware outage, Fault Tolerance automatically triggers fail over ensuring zero downtime and preventing data loss. vSphere Fault Tolerance is easy to set up and configure and does not require any other operating system and application specific agent and configurations. It is tightly integrated with vSphere and managed using the vSphere web client. Fault tolerance can support up to 4 vCPUs and 64 GB of memory thus providing protection for approximately 90% of mission critical customer workloads regardless of the application or operating system.
A traffic between hosts where primary and secondary virtual machines are running is referred as Fault Tolerance logging. In vSphere 6.0, Fault Tolerance logging is very bandwidth intensive and the use of a dedicated 10 GB of NIC on each host is recommended. Though this is not a requirement, without the necessary bandwidth, the protected virtual machine would be slower. vSphere 6.0 Fault Tolerance creates a copy of the entire virtual machine resulting in total protection for virtual machine storage, compute and memory. It also allows you to store primary and secondary VM files on both shared as well as on local storage. This result in increased protection, reduced risk and improved flexibility. You can use VMware snapshot based tools to backup the Fault Tolerance protected virtual machine enabling easier Backup Administration and Data Protectioin and Reduced Risks. Fault tolerance support all virtual disk types, including Eager-Zeroed Thick, Thick and Thin disks.
Host compatiblity for vSphere Fault Tolerance is now the same as for vSphere vMotion. These features make is easy to use Fault Tolerance.
vSphere Replication
vSphere Replication is a feature to provide data protection and disaster recovery for vSphere platform by replicating virtual machine within the same site of cross-site. It create a copy of the virtual machine that can be stored locally within a cluster or another site providing a data storage to rapidly restore the virtual machine within minute. This recovery process is simpler and faster as compared to the process of restoring from a backup. In vSphere 6.0, replication is tightly integrated with vSphere and is managed using vSphere web client. It allows you to create as many as 24 recovery points for a replicated VM. It also provides you with the option to minimize network bandwidth consumption by controlling the frequency and Extent of Replication. Further, the replicated data is compressed as it is sent across the network and stay compress until it is written to storage. Though compressing and decompressing them replicated data cost some CPU cycles on the source and target storage host, the result is always balanced between Performance, Compression and Limited overhead. vSphere 6.0 allows you to easily isolate network traffic associated with vSphere replication from other vSphere host traffic. This allows you to control bandwidth by configuring more and more NIC in a vSphere replication virtual appliance and by using vSphere network I/O control to separate network traffic. At the source, administrators can specify a NIC for replication traffic and use Network I/O control to control replication bandwidth utilization. At the target vSphere replication appliances can have multiple NICs with separate IP addresses to separate incoming traffic isolated controllable flows. The administrator can specify one of the NICs for incoming replication traffic to be written to storage and the result is improved performance and security.